Are Partners Responsible for the Company’s Debts and Taxes? ⚖️

The responsibility of companies for their debts and tax obligations is one of the fundamental pillars of commercial law. Determining whether partners are personally liable for these debts varies depending on the type of company and the legal system in each country.
Understanding this responsibility is crucial for:
✔️ Investors
✔️ Founders
✔️ Partners
✔️ Creditors
✔️ Executive managers
This knowledge helps prevent unexpected legal obligations that could affect personal assets or the company’s continuity.
🧱 1️⃣ Principle of Corporate Legal Personality
Before discussing liability, there is a fundamental principle:
🔹 The company is a separate legal entity from its partners.
🔹 It has its own financial assets.
🔹 It settles its debts under its own name.
🔹 Creditors cannot directly pursue the partners’ personal assets unless explicitly stated by law.
This principle is recognized in both Egyptian and Turkish law, forming the basis for determining legal responsibility. ⚖️
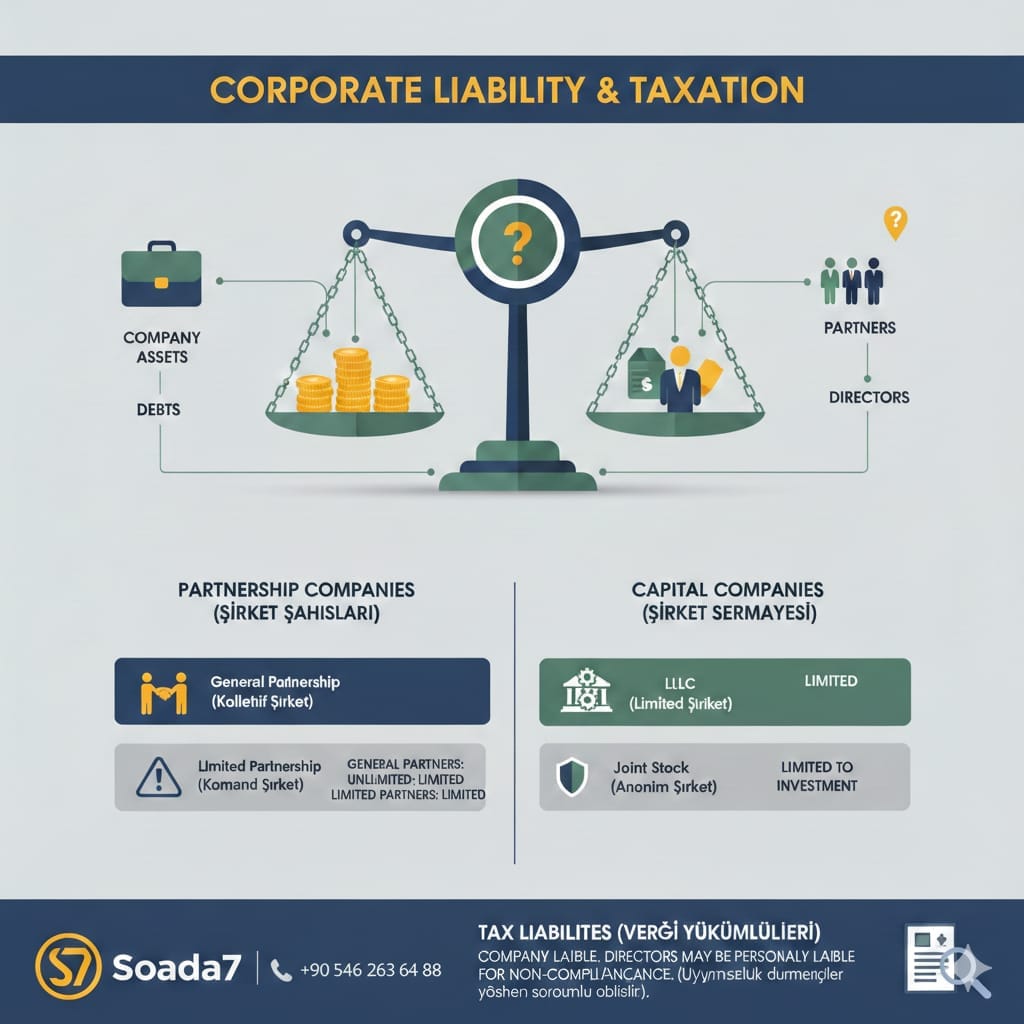
🧩 2️⃣ Types of Companies and How Liability Differs
The answer to the question “Are partners liable?” depends on the type of company, usually falling into the following categories:
🟡 A. Partnerships (Personal Companies)
a. General Partnership (شركة التضامن)
- Under Egyptian law, partners are jointly and severally liable for the company’s debts with their personal assets, not just their capital contribution.
- Creditors may claim the full debt from any partner or their personal assets.
- If the company goes bankrupt, the partners automatically face personal liability.
b. Limited Partnership (شركة التوصية البسيطة)
- Two types of partners:
✔️ General partners: fully liable, like in a general partnership.
✔️ Limited partners: liability is limited to their capital contribution and they cannot manage the company.
🔹 In older Turkish partnership models, liability was similarly joint, but these forms are less preferred due to the high personal risk for partners.
🟢 B. Capital Companies (Corporate Entities)
🔸 Limited Liability Company (LLC – شركة ذات مسؤولية محدودة)
📍 Egyptian law:
- Liability is limited to the partner’s committed capital contribution only.
- Creditors cannot pursue the partner’s personal assets beyond this limit.
📍 Turkish law:
- Under the Turkish Commercial Code (TTK), partners in an LLC are not personally liable for the company’s debts, only for their committed capital contribution.
- This is a key advantage of LLCs in protecting investors.
🔸 Joint Stock Company (شركة مساهمة)
- In both Egypt and Turkey, shareholders are liable only up to the value of their shares.
- Personal assets cannot be used to cover company debts.
📊 3️⃣ Taxes and Tax Debts
Tax obligations differ from commercial debts and may affect partners or managers directly:
🧾 ✅ Egyptian Law
- Taxes are imposed on the company as an independent legal entity.
- The company submits tax returns and pays taxes from its own budget.
- Partners are not personally liable except in cases of tax evasion, fraud, or abuse of the company’s legal personality.
🔎 Practical example: Failing to submit a tax return on time may result in fines or legal action, but it does not necessarily create personal liability for partners unless fraud is proven.
💠 📌 Turkish Law
- The law protects the company, but there is an important exception:
- If tax debts accumulate and company assets are insufficient, the tax authority can hold the manager or legal representative personally liable if they fail to fulfill tax obligations or refuse to pay.
- This risk does not apply to all partners but to those who manage and execute the company’s obligations.
🔎 This provides a strong legal incentive to comply with tax requirements and submit returns on time.
🧠 4️⃣ Liability of Managers and Legal Representatives
Even in LLCs or joint stock companies, partner immunity does not automatically extend to managers or representatives:
🚨 If a manager mismanages the company, causes significant losses, or refuses to pay taxes, personal liability may arise, allowing creditors or authorities to pursue their personal assets.
🏁 5️⃣ What Happens During Company Liquidation?
When a company is dissolved or liquidated:
- All debts, taxes, and creditor claims are settled first.
- If funds are insufficient:
✔️ In partnerships (personal companies): creditors can pursue partners based on the type of partnership.
✔️ In corporate entities: partners can only lose what remains unpaid from their capital contribution. - In Turkey, some regulations require partners to settle obligations before distributing remaining assets.
📌 6️⃣ Key Practical Recommendations
✔️ Choose the appropriate company type based on investment size and business activities.
✔️ Fully comply with tax obligations to avoid personal liability.
✔️ Keep company funds separate from personal assets.
✔️ Clearly document liability clauses in partnership agreements, especially in personal companies.
✔️ Appoint a qualified legal manager or accountant to avoid gaps in tax compliance.
✔️ Update the commercial registry promptly after any changes in partners or managers.

